10 Best Uninterruptible Power Supplies 2025 in the United States
Winner
Amazon Basics UPS Battery Backup & Surge Protector 600VA/360W, 8 Outlets, Standby Uninterruptible Power Supply, for Power Outage Protection, Compact, Black
The Amazon Basics UPS Battery Backup & Surge Protector provides 600VA/360W of power, making it a solid choice for home or small office use. Its power capacity is suitable for desktop computers, home networks, and entertainment systems, though it won't support heavy-duty equipment. With 8 outlets—4 surge-protected and 4 with both surge protection and battery backup—this UPS can accommodate several devices, offering basic protection against power surges and outages.
Most important from
13491 reviews
APC UPS, 1000VA Smart-UPS Lithium-Ion UPS with SmartConnect and NMC, SMTL1000RM2UCNC, Pure Sine Wave, Short-Depth 120V Uninterruptible Power Supply
The APC UPS, 1000VA Smart-UPS with SmartConnect and NMC offers reliable power backup with a capacity of 1000VA / 800W, making it suitable for small to medium-sized devices. It provides pure sine wave output, which is ideal for sensitive electronics. The unit includes 6 NEMA 5-15R battery backup outlets, allowing multiple devices to be connected simultaneously.
Most important from
23 reviews
Liebert GXT4 UPS w/Network Card - 6000VA/4800W 208V/120V, Online Double Conversion Rack Mount/Tower UPS, Uninterruptible Power Supply, Sine Wave, AVR, Battery Backup(GXT4-6000RT208)
The Liebert GXT4 UPS with Network Card is a robust uninterruptible power supply unit designed to provide reliable power protection for critical equipment. It boasts a substantial power capacity of 6000VA/4800W, ensuring that it can support high-demand devices. The online double-conversion technology is a major strength, as it conditions power continuously without drawing on the battery, which helps extend the battery's lifespan. Additionally, the UPS provides a pure sine wave output, which is ideal for sensitive electronics that require stable power delivery. With a transfer time of virtually zero, it ensures that connected equipment remains uninterrupted during power outages.
Top 10 Best Uninterruptible Power Supplies 2025 in the United States
Winner
Amazon Basics UPS Battery Backup & Surge Protector 600VA/360W, 8 Outlets, Standby Uninterruptible Power Supply, for Power Outage Protection, Compact, Black
Amazon Basics UPS Battery Backup & Surge Protector 600VA/360W, 8 Outlets, Standby Uninterruptible Power Supply, for Power Outage Protection, Compact, Black
Chosen by 1159 this week
APC UPS, 1000VA Smart-UPS Lithium-Ion UPS with SmartConnect and NMC, SMTL1000RM2UCNC, Pure Sine Wave, Short-Depth 120V Uninterruptible Power Supply
APC UPS, 1000VA Smart-UPS Lithium-Ion UPS with SmartConnect and NMC, SMTL1000RM2UCNC, Pure Sine Wave, Short-Depth 120V Uninterruptible Power Supply
Liebert GXT4 UPS w/Network Card - 6000VA/4800W 208V/120V, Online Double Conversion Rack Mount/Tower UPS, Uninterruptible Power Supply, Sine Wave, AVR, Battery Backup(GXT4-6000RT208)
Liebert GXT4 UPS w/Network Card - 6000VA/4800W 208V/120V, Online Double Conversion Rack Mount/Tower UPS, Uninterruptible Power Supply, Sine Wave, AVR, Battery Backup(GXT4-6000RT208)
apc by Schneider Electric SRT3000RMXLT 3kVA 208V Smart UPS SRT 12 Power Supply SRT3000RMXLT
apc by Schneider Electric SRT3000RMXLT 3kVA 208V Smart UPS SRT 12 Power Supply SRT3000RMXLT
Eaton 9SX 2000VA 1800W 120V Online Double-Conversion UPS - 6 NEMA 5-20R, 1 L5-20R Outlets, Cybersecure Network Card Option, Extended Run, Tower
Eaton 9SX 2000VA 1800W 120V Online Double-Conversion UPS - 6 NEMA 5-20R, 1 L5-20R Outlets, Cybersecure Network Card Option, Extended Run, Tower
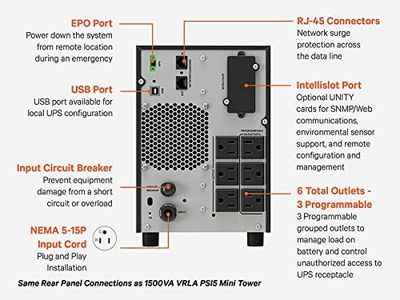
Vertiv Liebert PSI5 Lithium Ion UPS - 1920VA/1920W 120V 2U, Line Interactive, AVR, 0.9 Power Factor, Sine Wave, Uninterruptible Power Supply, Power Backup with Surge Protection (PSI5-2200RT120LI)
Vertiv Liebert PSI5 Lithium Ion UPS - 1920VA/1920W 120V 2U, Line Interactive, AVR, 0.9 Power Factor, Sine Wave, Uninterruptible Power Supply, Power Backup with Surge Protection (PSI5-2200RT120LI)
Liebert PSI5 Lithium-Ion UPS - 1500VA 1350W 120V, Line Interactive AVR Mini Tower Sine Wave UPS, 0.9 Power Factor Uninterruptible Power Supply(Battery Backup) with Surge Protection(PSI5-1500MT120LI)
Liebert PSI5 Lithium-Ion UPS - 1500VA 1350W 120V, Line Interactive AVR Mini Tower Sine Wave UPS, 0.9 Power Factor Uninterruptible Power Supply(Battery Backup) with Surge Protection(PSI5-1500MT120LI)
Vertiv Liebert GXT5 UPS - 2000VA/1800W 120V, Online Double Conversion, 2U Rack/Tower, Energy Star Certified, Lead Acid, Sine Wave, Battery Backup, 0.9 Power Factor, Colored LCD (GXT5-2000LVRT2UXL)
Vertiv Liebert GXT5 UPS - 2000VA/1800W 120V, Online Double Conversion, 2U Rack/Tower, Energy Star Certified, Lead Acid, Sine Wave, Battery Backup, 0.9 Power Factor, Colored LCD (GXT5-2000LVRT2UXL)
Tripp Lite Eaton Series 3000VA Smart UPS Back Up, Sine Wave, 120V, 3000W, 7 Outlets, 2U Rackmount or Tower, Network Card Option, LCD, USB, DB9, 3-Year Warranty & $250,000 Insurance (SMART3000RM2U)
Tripp Lite Eaton Series 3000VA Smart UPS Back Up, Sine Wave, 120V, 3000W, 7 Outlets, 2U Rackmount or Tower, Network Card Option, LCD, USB, DB9, 3-Year Warranty & $250,000 Insurance (SMART3000RM2U)
Our technology thoroughly searches through the online shopping world, reviewing hundreds of sites. We then process and analyze this information, updating in real-time to bring you the latest top-rated products. This way, you always get the best and most current options available.