10 Best Satellite Finders 2026 in the United States
Winner
DIRECTV AIM 2.0 Advanced Installation Meter for DIRECTV Satellite Dishes (AIM20)
The DIRECTV AIM 2.0 Advanced Installation Meter is designed specifically for aligning DIRECTV satellite dishes. One of its standout features is the step-by-step instructions, making it user-friendly even for those who are not experts. The ability to run Extended Installation Verification and various test modes can help identify and troubleshoot problems in cable runs efficiently.
Most important from
21 reviews
Winegard RT2035T RoadTrip T4 In-Motion RV Satellite Dish (DISH, DIRECTV, BellTV) - Fully Automatic RV Satellite Antenna
The Winegard RT2035T Roadtrip T4 In-Motion RV Satellite Antenna is a fully automatic roof-mounted antenna designed for RV enthusiasts. It stands out for its one-button operation, allowing for easy activation and deactivation. This model supports live TV viewing while traveling, which is ideal for road trips.
Most important from
132 reviews
Dish® Tailgater® Pro Premium Automatic Satellite TV System
The Dish® Tailgater® Pro Premium Automatic Satellite TV System is designed for people on the go, particularly RV owners and campers. It’s notable for its portability and ease of use, weighing just 7.39 kilograms and being lightweight enough for roof mounting. One of its standout features is the automatic locking mechanism, which simplifies setup by locking onto the satellite signal quickly and efficiently. This feature, combined with the on-screen prompts, makes it user-friendly, even for those not technically inclined.
Top 10 Best Satellite Finders 2026 in the United States
Winner
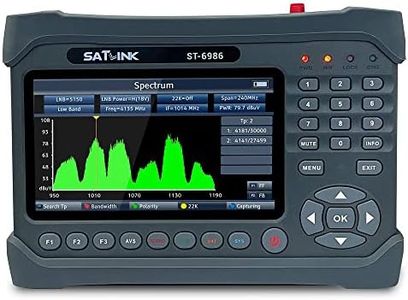
SATLINK ST-6986 Satellite TV Receiver DVB-S/S2/T/T2/C Combo Meter MPEG-4 HD H.265 (10bits) Spectrum Spectrum Analyzer Digital Satellite Finder Meter
SATLINK ST-6986 Satellite TV Receiver DVB-S/S2/T/T2/C Combo Meter MPEG-4 HD H.265 (10bits) Spectrum Spectrum Analyzer Digital Satellite Finder Meter
WS-6933 DVB-S/S2 FTA C&KU Band Satellite Meter Finder 2.4 inch LCD with Compass
WS-6933 DVB-S/S2 FTA C&KU Band Satellite Meter Finder 2.4 inch LCD with Compass
Our technology thoroughly searches through the online shopping world, reviewing hundreds of sites. We then process and analyze this information, updating in real-time to bring you the latest top-rated products. This way, you always get the best and most current options available.