10 Best Home Cell Signal Boosters 2025 in the United States
Winner
weBoost Home MultiRoom - Cell Phone Signal Booster | Boosts 4G LTE & 5G up to 5,000 sq ft for all U.S. Carriers - Verizon, AT&T, T-Mobile & more | Made in the U.S. | FCC Approved (model 470144)
The weBoost Home MultiRoom Cell Phone Signal Booster is a versatile and effective device designed to improve cell signal strength in homes up to 5,000 square feet, which typically covers 3-4 rooms. This makes it suitable for most residential setups, including those in rural areas, basements, or metal buildings. It supports all U.S. carriers, including Verizon, AT&T, and T-Mobile, ensuring that all users in your home benefit from better signal quality without any additional fees, as it operates within your current wireless plan. The product's FCC approval ensures compliance with regulatory standards, adding to its credibility and safety.
Most important from
2763 reviews
Amazboost Cell Phone Booster for Home, Cell Phone Signal Booster Kit, All U.S. Carriers -Compatible with Verizon, AT&T, T-Mobile, Sprint & More-5G 4G LTE 3G FCC Approved
The Amazboost Cell Phone Booster for Home is designed to enhance your cell phone signal, making it suitable for small homes, studios, apartments, or single rooms. It supports all major U.S. carriers like Verizon, AT&T, and T-Mobile, and works on multiple frequency bands including 3G, 4G LTE, and even some 5G signals. This means it can greatly improve both voice calls and data speeds, reducing dropped calls and offering better voice quality.
Most important from
2936 reviews
Cell Phone Booster for Home Office, Cover 8000 sq ft with 2 Indoor Antennas for All US Carriers, Cell Phone Signal Booster for Destination RV 4G 5G LTE Verizon AT&T T-Mobile APP Support FCC
The HiBoost Cell Phone Signal Booster is designed for home or office use, providing coverage up to 8000 square feet, which is ideal for larger spaces like homes with several rooms or metal buildings. With a gain of 70dB, it enhances signals from 1 grid to 3-4 grids, ensuring smooth phone calls and video streaming, making it a solid choice for families or small offices that need reliable connectivity. Its compatibility with all major US carriers (including Verizon, AT&T, and T-Mobile) and support for various signal types (2G, 3G, 4G, and 5G) make it versatile and suitable for most users.
Most important from
619 reviews
Top 10 Best Home Cell Signal Boosters 2025 in the United States
Winner
weBoost Home MultiRoom - Cell Phone Signal Booster | Boosts 4G LTE & 5G up to 5,000 sq ft for all U.S. Carriers - Verizon, AT&T, T-Mobile & more | Made in the U.S. | FCC Approved (model 470144)
weBoost Home MultiRoom - Cell Phone Signal Booster | Boosts 4G LTE & 5G up to 5,000 sq ft for all U.S. Carriers - Verizon, AT&T, T-Mobile & more | Made in the U.S. | FCC Approved (model 470144)
Chosen by 1123 this week
Amazboost Cell Phone Booster for Home, Cell Phone Signal Booster Kit, All U.S. Carriers -Compatible with Verizon, AT&T, T-Mobile, Sprint & More-5G 4G LTE 3G FCC Approved
Amazboost Cell Phone Booster for Home, Cell Phone Signal Booster Kit, All U.S. Carriers -Compatible with Verizon, AT&T, T-Mobile, Sprint & More-5G 4G LTE 3G FCC Approved
Cell Phone Booster for Home Office, Cover 8000 sq ft with 2 Indoor Antennas for All US Carriers, Cell Phone Signal Booster for Destination RV 4G 5G LTE Verizon AT&T T-Mobile APP Support FCC
Cell Phone Booster for Home Office, Cover 8000 sq ft with 2 Indoor Antennas for All US Carriers, Cell Phone Signal Booster for Destination RV 4G 5G LTE Verizon AT&T T-Mobile APP Support FCC
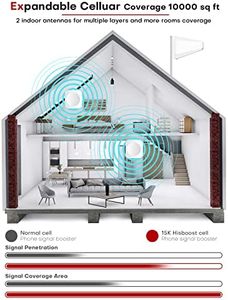
HiBoost Cell Phone Booster for Multiroom, Boost Cellular Signal up to 10,000 sq ft for All U.S. Carriers | Cell Phone Signal Boosters with 2 Inside Antennas Set for Homes & Offices 2-Story
HiBoost Cell Phone Booster for Multiroom, Boost Cellular Signal up to 10,000 sq ft for All U.S. Carriers | Cell Phone Signal Boosters with 2 Inside Antennas Set for Homes & Offices 2-Story
Cell Phone Booster for Home Office | Boosts 5G & 4G LTE | Cell Phone Signal Booster for All U.S. Carriers-Verizon, AT&T, T-Mobile & More | for Band 12/17,13,5,25/2,4 | HD Display | App | FCC Approved
Cell Phone Booster for Home Office | Boosts 5G & 4G LTE | Cell Phone Signal Booster for All U.S. Carriers-Verizon, AT&T, T-Mobile & More | for Band 12/17,13,5,25/2,4 | HD Display | App | FCC Approved
Cell Phone Signal Booster for Home up to 3000 Sq.Ft | Boost 4G 5G Cellular Signal Amplifier 65dB for T-Mobile, AT&T Verizon All U.S Carriers with 2 Indoor Antennas Band 12/17/13/5/25/2/4
Cell Phone Signal Booster for Home up to 3000 Sq.Ft | Boost 4G 5G Cellular Signal Amplifier 65dB for T-Mobile, AT&T Verizon All U.S Carriers with 2 Indoor Antennas Band 12/17/13/5/25/2/4
Hiboost Cell Phone Signal Booster for Home and Office, 4,000 sq ft, Boost 5G 4G LTE Data for Verizon AT&T and All U.S. Carriers, FCC Approved
Hiboost Cell Phone Signal Booster for Home and Office, 4,000 sq ft, Boost 5G 4G LTE Data for Verizon AT&T and All U.S. Carriers, FCC Approved
Cell Phone Booster for Home & Multi-Room,Up to 6500 sq ft,Cell Phone Signal Booster for Band 66/25/2/4/5/12/13/17,Boost 5G 4G Data for All U.S. Carriers FCC Approved Cell Booster
Cell Phone Booster for Home & Multi-Room,Up to 6500 sq ft,Cell Phone Signal Booster for Band 66/25/2/4/5/12/13/17,Boost 5G 4G Data for All U.S. Carriers FCC Approved Cell Booster
CEL-FI GO X G32 | Cell Phone Booster for Home | 4G, 5G, AT&T, Verizon & T-Mobile | Up to 15,000 Sq Ft Coverage | 100 dB Cell Phone Signal Booster | FCC Approved | 2 Antenna Kit
CEL-FI GO X G32 | Cell Phone Booster for Home | 4G, 5G, AT&T, Verizon & T-Mobile | Up to 15,000 Sq Ft Coverage | 100 dB Cell Phone Signal Booster | FCC Approved | 2 Antenna Kit
Our technology thoroughly searches through the online shopping world, reviewing hundreds of sites. We then process and analyze this information, updating in real-time to bring you the latest top-rated products. This way, you always get the best and most current options available.