10 Best Highest Quality 3D Printer 2025 in the United States
Winner
FLASHFORGE AD5X Multi-Color 3D Printer, CoreXY 600mm/s High-Speed, 1-Click Auto Leveling, 300°C Direct Drive Extruder, 220x220x220mm Build Volume, Ideal for Precision and Efficiency
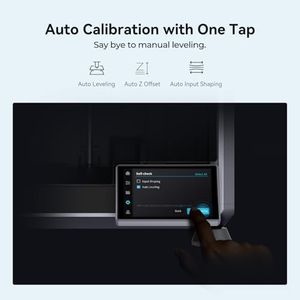
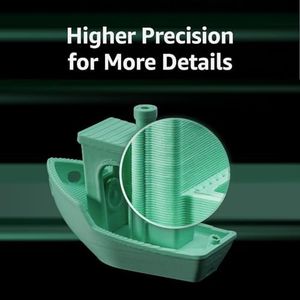
The FLASHFORGE AD5X is a high-quality 3D printer designed to deliver vibrant, multi-color prints with the ability to use up to four colors simultaneously. Its build volume of 220 x 220 x 220 mm is standard but may feel limited if you want to print very large objects. It stands out with a fast Core XY printing system reaching speeds up to 600 mm/s, which helps users complete projects quickly without sacrificing quality.
Most important from
82 reviews
FLASHFORGE Adventurer 5M 3D Printer with Fully Auto Leveling, Max 600mm/s High Speed Printing, 280°C Direct Extruder with 3S Detachable Nozzle, CoreXY All Metal Structure, Print Size 220x220x220mm
The FLASHFORGE Adventurer 5M 3D Printer stands out with impressive features tailored for high-quality 3D printing. Its fully auto-leveling system ensures hassle-free bed leveling, making it user-friendly even for beginners. The printer boasts a high print speed of up to 600mm/s, which is ideal for rapid prototyping and mass production, thanks to its Core XY structure and lightweight design.
Most important from
2812 reviews
Bambu Lab A1 3D Printer, Support Multi-Color 3D Printing, High Speed & Precision, Full-Auto Calibration & Active Flow Rate Compensation, ≤48 dB Quiet FDM 3D Printers 256 * 256 * 256mm³ Build Volume
The Bambu Lab A1 3D Printer stands out for its impressive combination of speed and precision, thanks to its ability to accelerate rapidly while maintaining detailed output. It supports multi-color printing when paired with the AMS lite system, which is a great plus if you want colorful and complex designs, though this accessory is sold separately unless you get the combo package. The printer offers a decent build volume of 256 x 256 x 256 mm, which is suitable for most hobbyist and intermediate projects. Its full-auto calibration feature makes it beginner-friendly by eliminating the usual manual setup headaches, and the active flow rate compensation helps produce smooth and consistent prints.
Most important from
264 reviews
Top 10 Best Highest Quality 3D Printer 2025 in the United States
Winner
FLASHFORGE AD5X Multi-Color 3D Printer, CoreXY 600mm/s High-Speed, 1-Click Auto Leveling, 300°C Direct Drive Extruder, 220x220x220mm Build Volume, Ideal for Precision and Efficiency
FLASHFORGE AD5X Multi-Color 3D Printer, CoreXY 600mm/s High-Speed, 1-Click Auto Leveling, 300°C Direct Drive Extruder, 220x220x220mm Build Volume, Ideal for Precision and Efficiency
Chosen by 1127 this week
FLASHFORGE Adventurer 5M 3D Printer with Fully Auto Leveling, Max 600mm/s High Speed Printing, 280°C Direct Extruder with 3S Detachable Nozzle, CoreXY All Metal Structure, Print Size 220x220x220mm
FLASHFORGE Adventurer 5M 3D Printer with Fully Auto Leveling, Max 600mm/s High Speed Printing, 280°C Direct Extruder with 3S Detachable Nozzle, CoreXY All Metal Structure, Print Size 220x220x220mm
Bambu Lab A1 3D Printer, Support Multi-Color 3D Printing, High Speed & Precision, Full-Auto Calibration & Active Flow Rate Compensation, ≤48 dB Quiet FDM 3D Printers 256 * 256 * 256mm³ Build Volume
Bambu Lab A1 3D Printer, Support Multi-Color 3D Printing, High Speed & Precision, Full-Auto Calibration & Active Flow Rate Compensation, ≤48 dB Quiet FDM 3D Printers 256 * 256 * 256mm³ Build Volume
Creality K2 Plus Combo 3D Printer, Multi Color Printing with New CFS, Max 600mm/s Printing Speed, Full-auto Leveling, Next-Gen Direct Drive Extruder, Dual AI Camera, Build Volume 350 * 350 * 350mm
Creality K2 Plus Combo 3D Printer, Multi Color Printing with New CFS, Max 600mm/s Printing Speed, Full-auto Leveling, Next-Gen Direct Drive Extruder, Dual AI Camera, Build Volume 350 * 350 * 350mm
FLASHFORGE Adventurer 5M Pro 3D Printer, 600mm/s High-Speed, FDM 3D Printer Auto Leveling with 280°C Quick Detachable Nozzle, Core XY Structure, Dual Filtration System, Print Size 220x220x220mm
FLASHFORGE Adventurer 5M Pro 3D Printer, 600mm/s High-Speed, FDM 3D Printer Auto Leveling with 280°C Quick Detachable Nozzle, Core XY Structure, Dual Filtration System, Print Size 220x220x220mm
Our technology thoroughly searches through the online shopping world, reviewing hundreds of sites. We then process and analyze this information, updating in real-time to bring you the latest top-rated products. This way, you always get the best and most current options available.